|

 Grizzly bears reach weights of 180-680 kg (400-1,500 lb); the male is on average 1.8 times as heavy as the female, an example of sexual dimorphism. Their coloring ranges widely across geographic areas, from blond to deep brown or black. These differences, once attributed to subspeciation, are now thought to be primarily due to the different environments these bears inhabit, particularly with regard to diet and temperature. Grizzly bears reach weights of 180-680 kg (400-1,500 lb); the male is on average 1.8 times as heavy as the female, an example of sexual dimorphism. Their coloring ranges widely across geographic areas, from blond to deep brown or black. These differences, once attributed to subspeciation, are now thought to be primarily due to the different environments these bears inhabit, particularly with regard to diet and temperature.
The Grizzly has a large hump over the shoulders which is a muscle mass used to power the forelimbs in digging. The head is large and round with a concave facial profile. In spite of their massive size, these bears can run at speeds of up to 55 km/h (35 mph).

Social: Normally a solitary, nocturnally active animal, in coastal areas the Grizzly congregates alongside streams and rivers during the salmon spawn. Every other year females (sows) produce one to four young (most commonly two) which are small and weigh only about 500 g (1 pound). Sows are very protective of their offspring.
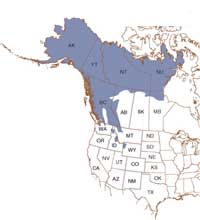 Range: The current range of the Grizzly bear extends from Alaska, down through much of Western Canada, and into the upper Northwestern United States including Idaho, Montana and Wyoming. Though it is originally native to a greater range than this, it is expected that the Grizzly's repopulation of its U.S. range will be a slow process due equally to the ramifications of reintroducing such a large animal to areas which are prized for agriculture and livestock and also because of the bear's slow reproductive habits. (Bears invest a good deal of time in raising young.) Range: The current range of the Grizzly bear extends from Alaska, down through much of Western Canada, and into the upper Northwestern United States including Idaho, Montana and Wyoming. Though it is originally native to a greater range than this, it is expected that the Grizzly's repopulation of its U.S. range will be a slow process due equally to the ramifications of reintroducing such a large animal to areas which are prized for agriculture and livestock and also because of the bear's slow reproductive habits. (Bears invest a good deal of time in raising young.)
 Diet: Being omnivores, grizzlies feed on a variety of plants and berries including roots or sprouts and fungi, as well as insects and smaller mammals; what is eaten depends largely on time of year and precise location. The larger bears have been known to prey on large mammals such as moose, sheep and caribou. Grizzly bears in general will feed on fish like salmon, trout, and bass, but those with access to a more protein-enriched diet in coastal areas can grow much larger than their herbivorous cousins. Diet: Being omnivores, grizzlies feed on a variety of plants and berries including roots or sprouts and fungi, as well as insects and smaller mammals; what is eaten depends largely on time of year and precise location. The larger bears have been known to prey on large mammals such as moose, sheep and caribou. Grizzly bears in general will feed on fish like salmon, trout, and bass, but those with access to a more protein-enriched diet in coastal areas can grow much larger than their herbivorous cousins.
Hibernation: In preparation for winter, bears will gain hundreds of kilograms of fat before going into a state of false hibernation. There is some debate amongst professionals as to whether or not Grizzly bears technically hibernate. Much of this debate revolves around body temperature and the ability for the bears to move around during hibernation on occasion. One interesting adaptation is that Grizzly bears have the ability to partially recycle their body wastes during this period. In some areas where food is plentiful all year round, Grizzly bears will forego hibernation altogether.

Prevent attack: Some travelers in bear country carry pepper spray or large caliber firearms to repel or kill an attacking bear. Once a pepper spray canister has been discharged, however, the odor of the pepper spray will actually attract bears. Grizzly bear cubs are excellent tree climbers, but after one year of age, they do not climb trees, making a tree an ideal refuge for humans unable to flee. Note that American Black bears (much smaller than Grizzly bears) are very good tree climbers.
Attack reason: A frequent reason for a sow to attack a human is that the sow thinks the human is threatening her cubs. In this case, the sow will attack to disable the threat and then typically leave. Hungry or ill bears may attack humans for other reasons and should be expected to behave differently.
Endangerd status: The Grizzly Bear is listed as threatened in the contiguous United States, and endangered in parts of Canada. It is currently slowly repopulating areas where it was previously extirpated. On January 9, 2006, the US Fish and Wildlife service proposed to remove Yellowstone grizzlies from the list of threatened and protected species.
Horribilis: Some biologists have argued that the word horribilis should be removed from the bear's taxonomic name, as its negative connotations may hinder conservation efforts. This change would not be permitted by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.
Trivia:
* Werner Herzog's 2005 film Grizzly Man deals with the story of Timothy Treadwell, a man who lived for over 13 years with Kodiak brown bears before being killed by them in Alaska.
* In April 2006, the first grizzly-polar bear hybrid found in the wild was discovered at Banks Island, Canada.
All text is available under the terms
of the GNU Free Documentation License
|

