|
Denmark
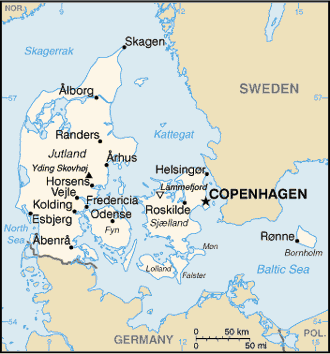
The Kingdom of Denmark (Danish: Kongeriget Danmark) is geographically the smallest Nordic country and is part of the European Union. It is located in Scandinavia, which is in northern Europe. Denmark borders the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, and consists of a peninsula attached to Northern Germany named Jutland (Jylland in Danish), the islands Funen (Fyn), Zealand (Sjælland), Bornholm and many smaller islands. Denmark is north of Germany, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway. Greenland and the Faroe Islands are The Crown of Denmark's territories, each with political home rule. The origin of Denmark is lost in prehistory. Prior to being populated by Scandinavians, Denmark was home to Celts - as evidenced by the discovery of ritualistic bog murders and burials. The oldest Danevirke is from the 7th century, at the same time as the new Runic alphabet. Up into the 11th century the Danes were known as Vikings, together with Norwegians and Swedes, colonising, raiding and trading in all parts of Europe. Many archaeologist and historians believe that the Viking even made it as far as America. They traveled from Scandinavia to Iceland, then further to Greenland and then finaly America. At various times Denmark has ruled parts of England and Ireland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland and parts of the Virgin Islands, Tranquebar in India, parts of the Baltic coast and what is now northern Germany. Scania, Blekinge and Halland were part of Denmark for most of its early history, but were lost to Sweden in 1658. The union with Norway was dissolved in 1814, when Norway entered a new union with Sweden (until 1905). The Danish liberal and national movement gained momentum in the 1830s, and after the European revolutions of 1848 Denmark became a constitutional monarchy June 5, 1849.
After the Second War of Schleswig in 1864 Denmark was forced to cede Schleswig-Holstein to Prussia, in a defeat that left deep marks in the Danish national identity. After this point Denmark adopted a policy of neutrality, following which Denmark stayed neutral in World War I. On April 9, 1940, Denmark was invaded by Nazi Germany (Operation Weserübung) and remained occupied throughout World War II, despite some internal resistance. After the war, Denmark became a member of NATO and, in 1973, the European Economic Community (later, the European Union).
This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Denmark". |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||