Poland
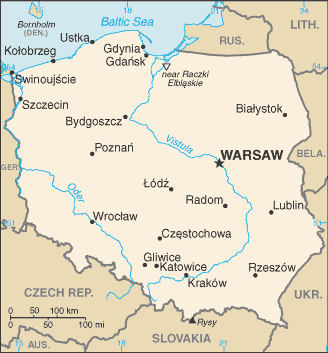
The Republic of Poland is a country located in Central Europe, between Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and the Baltic Sea, Lithuania and Russia (in the form of the Kaliningrad Oblast exclave) to the north. The Polish nation started to form into a recognisable unitary territorial entity around the middle of the 10th century under the Piast dynasty. In 12th century Poland was fragmented into several smaller states, which were later ravaged by the Mongol armies of Golden Horde in 1241. Under the Jagiellon dynasty Poland forged an alliance with its neighbor Lithuania. A golden age occurred in the 16th century during its union (Lublin Union) with Lithuania in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The citizens of Poland took pride in their ancient freedoms and parliamentary system, though the Szlachta monopolised the benefits thereof. Since that time Poles have regarded freedom as their most important value. Poles often call themselves the Nation of the free people. In mid-17th century a rebellion of Cossacks led by Bohdan Chmielnicki ushered in the turbulent time known as "The Deluge" (potop). Numerous wars against Ottoman Empire, Russia, Sweden, Transylvania and Brandenburg-Prussia ultimately came to an end in 1699. During the following 80 years, the waning of the central government and deadlock of the institutions weakened the nation, leading to dependency on Russia. The Enlightenment in Poland fostered a growing national movement to repair the state, resulting in the first written constitution in Europe, in 1791 (May Constitution of Poland). The process of reforms ceased with the partitions of Poland between Russia, Prussia, and Austria in 1772, 1793 and 1795; these ultimately completely dissolved Poland. Poles resented their shrinking freedoms and several times rebelled against their oppressors. After the Napoleonic wars a reconstituted Polish state, the Duchy of Warsaw, ruled by the Russian tsar as a Congress Kingdom, possessed a liberal constitution. However, the Russian tsars soon reduced Polish freedoms and Russia eventually de facto annexed the country. Later in the 19th century, Austrian-ruled Galicia became the oasis of Polish freedom. During World War I all the Allies agreed on the restitution of Poland that United States President Woodrow Wilson proclaimed in point 13 of his Fourteen Points. Shortly after the surrender of Germany in November 1918, Poland regained its independence as the Second Polish Republic. A new threat, Soviet aggression, arose in the 1919 (Polish-Soviet War), but Poland succeeded in defending its independence. The Second Polish Republic lasted until the start of World War II when Germany and the Soviet Union invaded and split the Polish territory between them from (September 28, 1939). Poland suffered greatly in this period. Of all the countries involved in the war, Poland lost the highest percentage of its citizens: over 6 million perished, half of them Polish Jews. Poland's borders shifted westwards; pushing the eastern border to the Curzon line and the western border to the Oder-Neisse line. After the shift Poland emerged smaller by 76 000 km² or by 20% of its pre-war size. The shifting of borders also involved the migration of millions of people – Poles, Germans, Ukrainians, Jews. Eventually, Poland became, for the first time in history, an ethnically unified country. The Soviet Union brought a new communist government to Poland, analogously to much of the rest of the Eastern Bloc. In 1948 a turn towards Stalinism brought in the beginning of the next period of totalitarian rule. The People's Republic of Poland was officially proclaimed in 1952. In 1956 the régime became more liberal, freeing many people from prison and expanding some personal freedoms. Labour turmoil in 1980 led to the formation of the independent trade union, "Solidarity", which over time became a political force. It eroded the dominance of the Communist Party; by 1989 it had triumphed in parliamentary elections, and Lech Wałęsa a Solidarity candidate eventually won the presidency. A shock therapy program during the early 1990s enabled the country to transform its economy into one of the most robust in Central Europe. Despite the regression in levels of social and economic human rights standards, numerous improvements in other human rights standards occurred (free speech, functioning democracy and the like). Poland was the first among post-communist countries to regain pre-1989 GDP levels. Poland joined the NATO alliance in 1999. Following a massive advertising campaign by the government in favour of joining the European Union, Polish voters voted yes to the EU in a referendum in June 2003. Poland joined the European Union on 1 May 2004.
This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Poland". |
||||||||||